ADHD Assessment and Diagnosis
1. Psychosocial Assessment
We will explore variables related to psychosocial history, developmental milestones, family history and dynamics, educational/occupational history, and social-emotional well- being to gain a comprehensive understanding of the variables contributing to your ADHD symptoms.
2. Symptom Evaluation
We use valid and reliable questionnaires and interviewing to assess for common ADHD symptoms, as well as differentiate between ADHD and other diagnoses. This process also helps us understand the severity of your symptoms, their impact on your life, and how to best support you.
Many children with ADHD struggle with inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
These symptoms can impact academic performance, social interactions, and
daily activities.
Children with ADHD may have difficulty focusing on tasks, completing
assignments, or following instructions. They might also interrupt conversations,
fidget, or have trouble regulating their emotions.
Adults with ADHD often experience challenges with focus, organization, and
emotional regulation. They may struggle to prioritize tasks, manage time
effectively, and maintain a consistent work flow.
In addition, adults with ADHD may experience difficulty with impulsivity, such as
making rash decisions or engaging in risky behaviors. They may also have
trouble regulating their emotions, leading to frustration, anger, or anxiety.
3. Neurocognitive Testing
We use valid and reliable neurocognitive testing to identify cognitive strengths and weaknesses. Our neurocognitive testing assesses a variety of neurocognitive domains related to ADHD, including:
- Simple Attention
- Complex Attention
- Sustained Attention
- Executive Function
- Cognitive Flexibility
- Working Memory
- Verbal & Visual Memory
- Processing Speed & Reaction Time
- Motor & Psychomotor Speed
- NeuroCognition Index
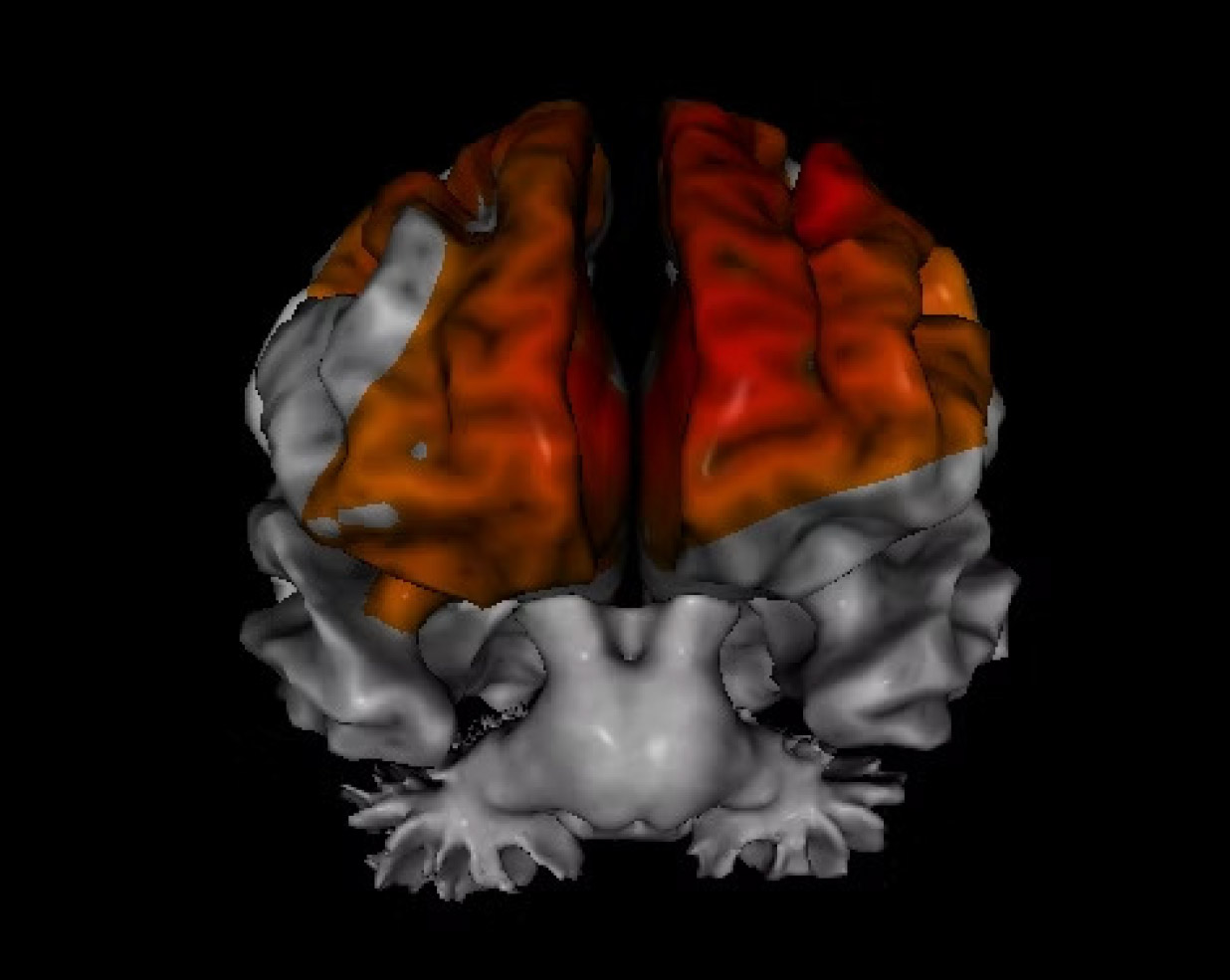
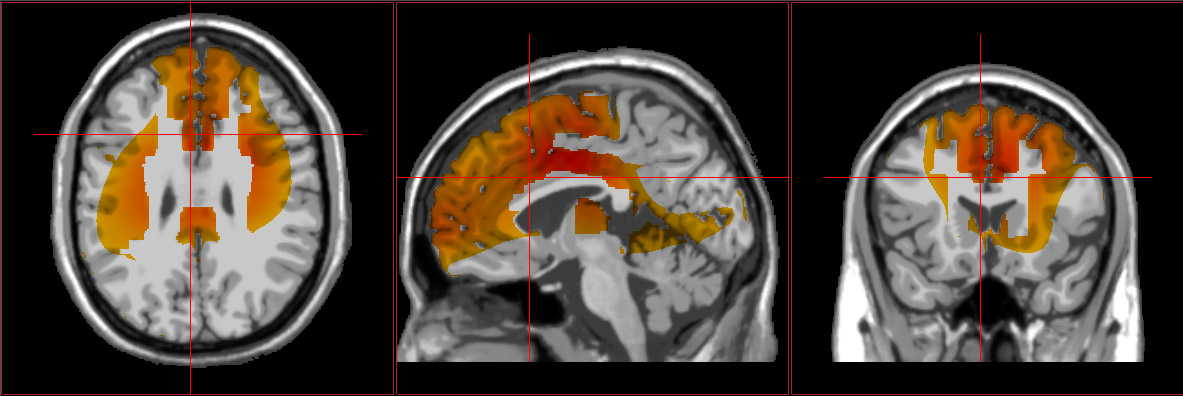
4. Functional Neuroimaging
We utilize a combination of non-invasive functional imaging modalities, including EEG, QEEG, and swLORETA, to assess brainwave patterns underlying symptomatology and guide personalized recommendations based on your individual brain phenotype.
Electroencephalography (EEG) and quantitative EEG (QEEG) are non-invasive
neuroimaging techniques that measure brain electrical activity. They help us
assess brain function, including attention, impulsivity, and executive function, as
well as differentiate from other mental health and/or learning challenges.
Source-localized electroencephalography (sLORETA) is a neuroimaging
technique that uses EEG data to localize the source of brain activity in specific
regions. It helps us understand the underlying neural roots of symptoms and
specific areas of dysfunction.
This neuroimaging can also assist with determining the most effective treatment
interventions, including which medications and/or supplements could be
beneficial, as well as neurotherapy protocols and other interventions designed to
improve functioning within regions showing impairment.