WHAT THE RESEARCH SAYS
Anxiety and panic disorders are the most common mental health concerns in the world. They can affect a person’s ability to work, interact with others, experience new things, or complete tasks necessary for growth and survival. Due to the prevalence of anxiety, a great deal of research has been done to better understand related underlying mechanisms and the most effective treatments. Research suggests that neurotherapy and other integrative modalities can be effective, non-invasive approaches for reducing anxiety.
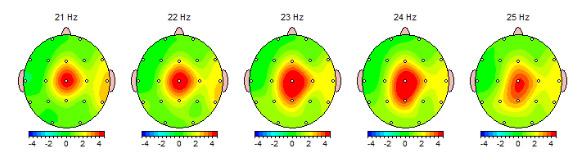
In one study, 14 participants were asked to complete a pre- and post-intervention self-report anxiety measure (Dreis, Groufer, Perez, Ruso, Fitzsimmons, & Jones, 2015). They were provided with two 30 minute sessions of QEEG amplitude neurofeedback per week for 14 weeks. At the conclusion of the study, researchers found statistically significant improvements in participants’ scores, implying a reduction in anxious symptoms and suggesting that this form of neurotherapy can provide clinically meaningful relief from anxiety and panic.
- Dreis, S. M., Gouger, A. M., Perez, E. G., Ruso, G. M., Fitzsimmons, M. A., Jones, M. S. (2015) Using Neurofeedback to Lower Anxiety Symptoms Using Individualized qEEG Protocols: A Pilot Study. NeuroRegulation 2(3), 137-148.
An additional study questioned whether combining heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback with neurofeedback could help to reduce symptoms of anxiety among participants. Brain activity, blood pressure, breathing patterns, HRV, and self-reported psychological symptoms were measured with each participant before and after the study. Results showed reductions in overall anxiety symptoms and significant changes in EEG brainwave patterns, as well as breathing rate, HRV, and blood pressure. By addressing the connection between the brain and body, it appears that combining HRV and neurofeedback training can effectively address the roots of anxiety to provide significant relief.
- White, E. K., Groeneveld, K. M., Tittle, R. K., Bolhuis, N. A., Martin, R. E., Royer, T. G., Fotuhi, M. (2017) Combined Neurofeedback and Hearth Rate Variability Training for Individuals with Symptoms of Anxiety and Depression: A Retrospective Study. NeuroRegulation 4(1) 37-55.
For more studies on neurotherapy for Anxiety, see our Research page.